Nutrition for lactose intolerant patients What does a lactose intolerant patient eat?

70% of adults worldwide suffer from a deficiency – to varying degrees – in the production of the enzyme lactase. Which may lead to lactose intolerance, also known as “lactose intolerance.”Lactose intolerance“. A special approach to feeding lactose intolerant patients is the cornerstone of the treatment regimen.
What is lactose intolerance? What are its causes and types? How is it diagnosed? What is the best diet for lactose intolerant patients? This is what we will discuss in the following lines.
What are the symptoms of lactose intolerance?
By lactose intolerance, we mean the body’s inability to digest lactose, which is a natural sugar found in milk and its various derivatives. This leads to the appearance of many symptoms such as:
- Stomach pain and painful cramps.
- Feeling bloated.
- Mild or severe diarrhea.
- Increased abdominal gas.
- Nausea and vomiting.
The severity of these symptoms varies from very mild to severe and annoying, depending on the degree of lactase deficiency. It usually begins to appear after consuming milk or any of its derivatives for a period ranging from 30 minutes to two hours.
What is the difference between dairy and lactose intolerance?
Lactose allergy is a common condition among adults, and it differs from milk allergy, as milk allergy – like other types of food allergies – results from the reaction of the immune system towards a specific type of food. Which causes symptoms such as: skin rash and itching.
While lactose allergy occurs due to a problem in the digestive system, not the immune system.
It should be noted that sometimes lactose sensitivity is called by another name, which is lactose intolerance.
This leads us to talk about the causes and types of lactose intolerance.
Causes of lactose intolerance
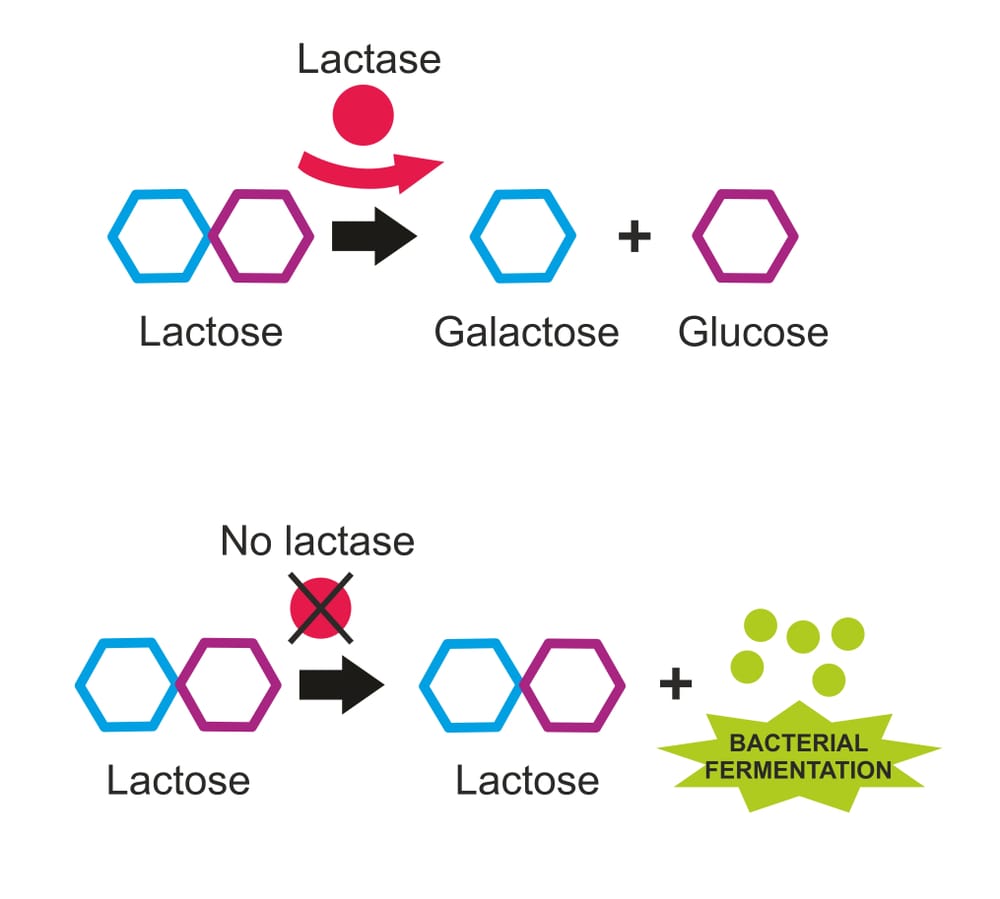

Low levels of the enzyme lactase in the intestines are the main cause of lactose intolerance..
It is the enzyme secreted from the villus of the small intestine, which is responsible for breaking down lactose (disaccharides) into glucose and galactose (simple sugars that can be easily absorbed). In case of deficiency, lactose remains undigested, so bacteria ferment it, producing water and hydrogen. This leads to the appearance of symptoms associated with lactose intolerance. Factors that contribute to lactase deficiency include:
- Genetic factors: It is characterized by the complete absence of the lactase enzyme.
- Acquired factors: It is common and widespread, like some diseases of the digestive system.
Lactose intolerance may be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying cause of the lactase enzyme deficiency. Most cases that appear in adults are inherited and often last a lifetime. As for cases that appear in children, they are often due to an infection in the digestive system, and may last for only a few weeks.
There are four main types of lactose intolerance:
Types of lactose intolerance
- Primary lactose intolerance: It is the most common type. It results from a decrease in lactase production as a result of a lack of dependence on milk and its products, after the age of two and weaning. Symptoms may not be noticeable until adulthood. This type is partly due to genes. Population studies indicate that it affects 5-17% of Europeans, about 44% of Americans, and 60-80% of Africans and Asians.
- Secondary lactose intolerance: It occurs due to exposure to intestinal infections and problems in the digestive tract. Which affects the cells that produce the lactase enzyme in the intestine. Treating the main cause usually restores lactase levels and improves symptoms.
- Congenital lactose intolerance: It is a rare occurrence, in which children are born with lactose intolerance resulting from the absence of the lactase enzyme due to a genetic factor (both parents have the same genetic defect).
- Developmental lactose intolerance: It happens to some premature babies (those born before the 37th week of pregnancy); Because their intestines are not yet complete when they are born. It is a temporary condition; The condition of infants improves as they grow older.
If lactose intolerance is suspected, a specialist doctor should be consulted before excluding milk and its derivatives from the diet. In order for the diagnosis to be made correctly, we must use tests for lactose intolerance.
How is lactose intolerance diagnosed?


As we know, diagnosing diseases usually requires performing some tests, and here, we will talk more deeply about the types of lactose intolerance tests.
The diagnosis of lactose intolerance begins with the appearance of symptoms of the disease and the response to reducing the amounts of milk and its derivatives in the diet.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may perform some tests, such as:
- Hydrogen Breath Test: It is the most common test. During the test, your doctor will direct you to drink a liquid that contains lactose. Then, the amount of hydrogen in your breath after exhalation is measured in a balloon-like device at specific time intervals. A large amount of hydrogen indicates an inability to digest and absorb lactose.
- Lactose tolerance test: This test also requires drinking a liquid containing lactose, then measuring the glucose level in the blood two hours later. If the blood glucose level does not rise, this means the inability to digest and absorb lactose.
- Stool acidity test: This test is usually performed on infants and young children; This is due to the difficulty of undergoing previous examinations. It detects the presence of lactic acid in a stool sample. Its presence indicates that lactose is fermenting in the intestine and not being digested properly.
After confirming the diagnosis, and knowing that there is no radical treatment for lactose intolerance, the method used for treatment depends on monitoring the nutrition of lactose intolerant patients in several ways.
We also receive some questions about the name of the milk allergy test, and the answer is that there is no test specifically for milk allergy only, but rather they are the same tests for lactose intolerance.
Nutrition for patients with lactose intolerance
Here we present some methods used in feeding lactose intolerant patients:
- Reducing or eliminating foods containing lactose from the diet.
- Resorting to replacing the nutrients in milk and its derivatives from other sources.
- Taking the lactase enzyme as a medication (dietary supplement).
- Using specific bacteria (probiotics) found in some types of yogurt to help digest lactose.
If lactose intolerance is caused by another medical condition, treating that condition may help restore the body’s ability to digest lactose, even after a period that may extend to months. To overcome annoying symptoms, attention must be paid to the nutritional patterns of lactose intolerant patients. Therefore, it is recommended to follow a low-lactose diet.
Diet for people with lactose intolerance


Nutrition for patients with lactose intolerance is based on the basic principle of reducing or excluding foods containing lactose from the diet. The amount of lactose in food can be reduced by reducing the daily portion of milk and dairy products. You can also eat lactose-free or low-lactose products.
In the following paragraphs, we present a comprehensive guide to the question: What does a lactose intolerant patient eat?
Foods prohibited for a lactose intolerant patient:
Contraindications for lactose intolerance
- Cow and goat milk.
- Cheese.
- Ice cream.
- Butter.
- Yogurt.
- Dry milk (powder).
- Pudding and custard.
- Whipped cream and coffee creamer.
- Drinks that are prepared on milk, such as some juices.
Fruits containing lactose
Some people ask which fruits contain lactose so that they can avoid them, but in fact, lactose is milk sugar.
This means that it is found in milk and dairy products and what is made from them.
Therefore, all fruits and vegetables are lactose-free.
Do bananas contain lactose? ؟
Bananas or any fruit do not contain lactose, as lactose is milk sugar, as we mentioned in the previous paragraph.
Does Cerelac contain lactose?
In the context of talking about treating lactose intolerance for infants, mothers often ask whether Cerelac contains lactose or not.
We assure you, Madam, that Cerelac (without milk) is free of lactose and gluten.
Foods containing small amounts of lactose:
- Bread and baked goods.
- Milk chocolate.
- Dry breakfast cereals.
- Prepared meat.
- Margarine butter.
- Some sauces (containing cream).
- Desserts and pancake mixes.
- Biscuits and cakes.
- Some quick preparation foods, such as: noodles of all kinds.
Also, some medications and nutritional supplements contain lactose, such as: antacids, anti-flatulence agents, and some vitamins.
Therefore, caution must be taken and people with lactose intolerance should avoid forbidden foods. On the other hand, there are lactose-free foods that have great and varied nutritional benefits. Therefore, it is recommended to consume it safely and without fear. This is what we will discuss in the following.
Lactose-free foods:


Many healthy foods fit easily into a lactose-free diet, examples of which include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds and legumes. Here’s the detail:
- fruits: Oranges, apples, grapes, pineapple, mango and plum.
- Vegetables: Garlic, onions, spinach, arugula, broccoli, carrots, and zucchini.
- Meat: Beef, lamb and veal.
- Poultry: Chicken, duck, geese and turkey.
- Fish: Tuna, salmon, mackerel, sardines and salmon.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas and all kinds of beans.
- Nuts: Walnuts, almonds, cashews, pistachios and hazelnuts.
- Seeds: Flax, sunflower, pumpkin and chia seeds.
- Whole grains: Barley, flour, oats and quinoa.
- Healthy fats: Olive, sesame, coconut and avocado oils.
- Herbs and spices: turmeric, thyme, rosemary, basil, and mint.
With regard to children’s nutrition, you should not deprive the child of the many benefits found in milk and its products. Cow’s milk can be replaced with lactose-free milk or calcium-fortified milk, such as:
- Soy milk.
- Rice milk.
- Coconut milk.
- Oat milk.


It is also possible to resort to alternatives rich in some nutrients found in milk, especially calcium and vitamin D. This is to compensate for the deficiency or absence of milk as a source of these nutrients. Milk alternatives rich in calcium include:
- Sesame.
- Flax seeds.
- Almonds.
- Dried beans.
- Spinach and broccoli.
- Sardines, salmon and sea oysters.
Regarding vitamin D, the best way to obtain it is direct exposure to sunlight. As well as eating fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, tuna and mackerel.
In conclusion, the nutrition of lactose intolerant patients is one of the most important things that should be taken into account when dealing with those suffering from it.
It is a medical condition that may last a lifetime, and requires adjustments to the diet. There is no cure for lactose intolerance, but symptoms can be prevented or reduced by avoiding milk and dairy products, or by taking the lactase enzyme in medicinal form, as well as other alternatives that are becoming increasingly popular. Eating these alternatives also helps compensate for the absence of some nutrients that are naturally found in milk.




